Kronprins Haakon icebreaker
Kronprins Haakon icebreaker current position
The current location of Kronprins Haakon icebreaker is in North East Atlantic Ocean (coordinates 78.61556 N / 21.03885 E) cruising en route to SJ LYR. The AIS position was last reported 58 seconds ago.
Current PositionSpecifications of Kronprins Haakon icebreaker
| Year of build | 2017 / Age: 8 |
| Flag state | Norway |
| Builder | Fincantieri / Riva Trigoso-Muggiano shipyards (La Spezia, Italy), VARD (Langsten, Norway) |
| Class | PC3 diesel icebreaker |
| Building cost | EUR 175 million |
| Engines (power) | Rolls-Royce (17 MW / 22797 hp) |
| Propulsion power | 13.2 MW / 17701 hp |
| Speed | 15 kn / 28 km/h / 17 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 100 m / 328 ft |
| Beam (width) | 21 m / 69 ft |
| Gross Tonnage | 9145 gt |
| Passengers | 38 |
| Crew | 17 |
| Cabins | 38 |
| Owner | Norway (Norwegian Polar Institute) |
| Operator | IMR (Norwegian Institute of Marine Research) |
Kronprins Haakon icebreaker Review
Review of Kronprins Haakon icebreaker
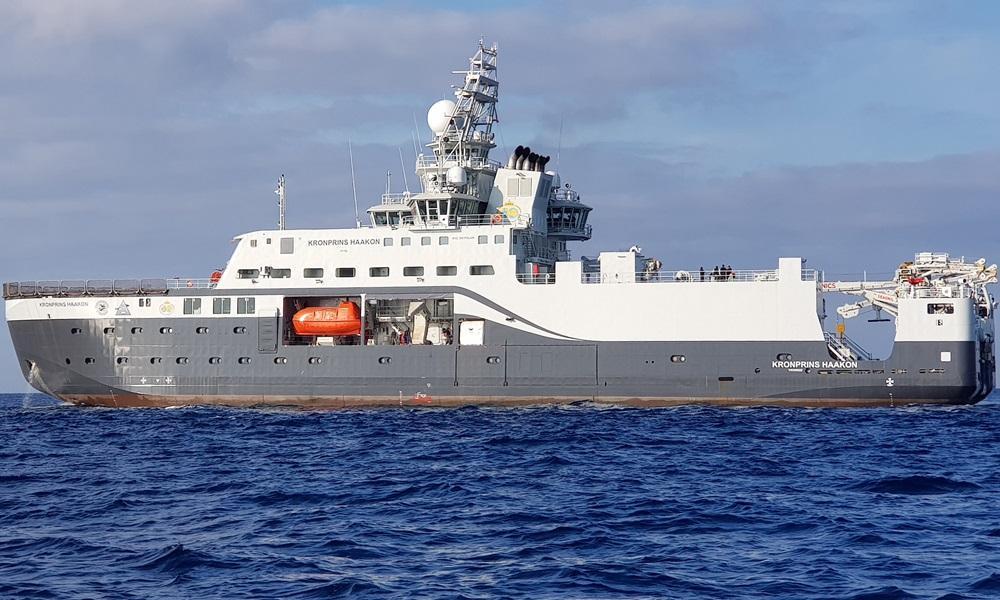
The 2017-built RV Kronprins Haakon is an icebreaking vessel for polar research. The icebreaker is owned by Norwegian Polar Institute (Norway) and operated by IMR-Norwegian Institute of Marine Research (owned by Norway's Ministry of Fisheries and Coastal Affairs). The ship's main user is the University of Tromso (aka "Arctic University of Norway").
With GT-tonnage/volume 9000 tons, Kronprins Haakon is Norway's largest icebreaker ever built. The vessel will operate mainly in the Barents Sea (Arctic Ocean waters, to the north of Norway and Russia).
The vessel (IMO number 9739587) is currently Norway-flagged (MMSI 257275000) and registered in Oslo.
History and construction
The new polar research vessel concept was proposed in 1999, with the feasibility study completed in 2007. In 2008, Rolls-Royce Marine won the design contract. The initial design concept was further developed via cooperation with the Norwegian Polar Institute. In 2011, the Norwegian Ministry of Finance approved the design (UT 395 project).

In 2012, the Norwegian Parliament approved the ship's construction funding and included it in the country's 2013 budget. The shipbuilding contract was signed with Fincantieri (Italy) on December 19, 2013. Construction works were done at Fincantieri's covered drydock at the shipyard Riva Trigoso (Muggiano, near Genoa). Final outfitting works were carried out at Fincantieri's Langsten shipyard (VARD, Norway).
RV Kronprins Haakon vessel details and technology
The icebreaker features latest technology equipment for polar surveys (acoustic, seismic, subsea), including ADCP (acoustic), echo sounder, biological echo sounder, biological sonar, omnidirectional sonar, monitoring systems, meteo weather station, cargo handling facilities, airborne robots, scientific moon pool, ROVs and AUVs (remotely operated and autonomous underwater vehicles / robotic submarines), kayaks (large-capacity inflatable boats).
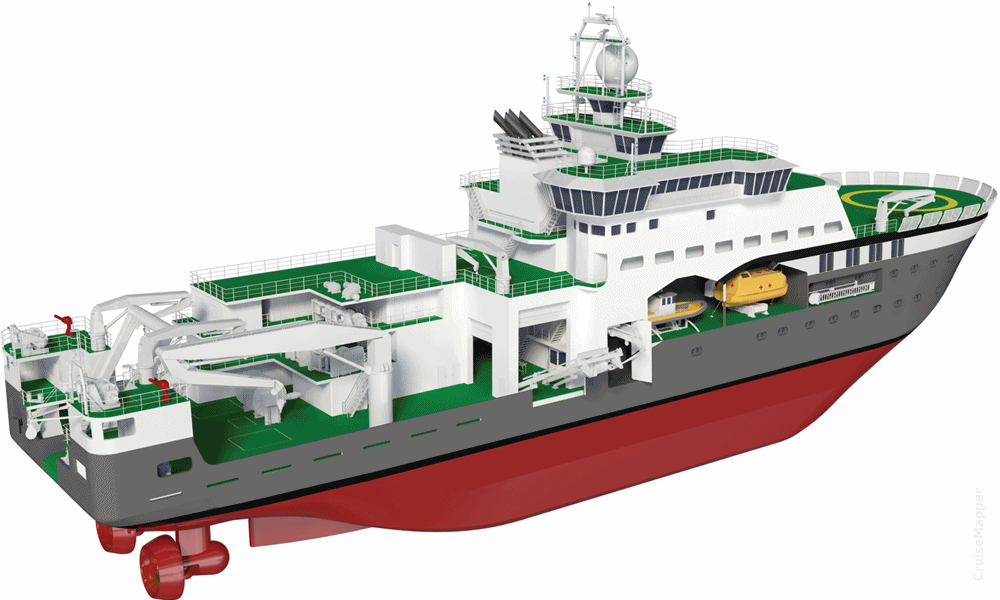
Other onboard facilities include electric winches (mechanical devices), containerized labs and workshops, dedicated scientific research facilities, passenger staterooms, general lounge (mess hall), galley (kitchen), bar lounge, conference room/library, sauna room, gym room, laundries, hospital (resident doctor).
The ship is powered by four Rolls-Royce marine diesel engines (total power output 17 MW)), of which two are two 9-cylinder and two 6-cylinder.
Kronprins Haakon has 38 staterooms for 55 personnel (passengers plus crew). The vessel features a helicopter hangar (capacity 2 smaller helicopters) and a bow-located helipad that can be used by larger helicopters.
Like all new-design icebreaking vessels, the ship has diesel-electric propulsion. The system consists of diesel powerplant (4 engines), two azimuth thrusters (twin Z-drives, total power output 11 MW) and two bow thrusters (total power output 2,2 MW).
Kongsberg Maritime was the supplier of the ship's automation and control systems, as well of its dynamic positioning system, K-Bridge, and deck handling systems.
Max draft is 8 m (26 ft), the icebreaking capacity is 1,5 m (5 ft). The ship's speed when breaking through 1 m (3 ft) thick ice is 5 kN (9 kph / 6 mph).
- Cargo capacity: cargo hold (1180 m3), TEU containers (20)
- Bollard pull (pulling/towing power): 158 tons
- Ice-class PC3 (IACS, hull) allowing year-round operations in 2nd-year ice
- Range: 28000 km (17000 mi)
- Endurance: 65 days
The ice-strengthened hull allows safe navigation in winter ice and temperatures down to - 35 C (- 31 F).
The ship can maintain a cruising speed of 12 knots (22 kph / 14 mph) in ice thickness 0,4 m (16 in).
On Main Deck 3 are located most of the ship's research facilities (oceanography, marine biology, geology), including 15 fixed labs, 3 container labs, refrigerated storage rooms, Working Deck (cranes, aft A-frame for trawling, winches), a helicopter hangar.
The vessel has a scientific moon pool (aka "wet porch") sized 3x4 m / 10x13 ft. This is a floor opening in the hull that gives direct access to the water below and allows the crew to deploy underwater instruments (including ROVs and AUVs).
Like all ice-breaking research vessels, Kronprins Haakon is unique with its ability to collect data in ice conditions. This is achieved with two retractable keels, but they can't be deployed while the ship is breaking the ice.
Kongsberg Maritime manufactured survey technology equipment includes multi-beam echo sounders (EM 302, EM 710), single beam echosounder (EA 600), Sub-Bottom Profilers (SBP300, TOPAS), High Precision Acoustic Positioning System (HiPAP 501), Simrad scientific systems (EK80 single beam, multibeam ME70 and MS70), omnidirectional sonars (SH90), Simrad FX80 (trawl monitoring / live camera feed).
Note: In the case of poor AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's current location is impossible. You can see CruiseMapper's list of all icebreakers and ice-breaking research ships in the "itinerary" section of our Icebreakers hub. All states and their fleets are listed there.
Kronprins Haakon icebreaker ship related cruise news
- Cruise Industry

Ponant's Le Commandant Charcot ship teams up with icebreaker Kronprins Haakon in the Arctic
In the Arctic, Ponant's cruis ship Le Commandant Charcot (aka Ponant Icebreaker) is currently leading the way (satellite AIS tracking) to Kronprins...
August 1, 2022 - show more news
Kronprins Haakon icebreaker Wiki
The vessel's construction was (hull and superstructure building) was completed at Fincantieri's shipyards Riva Trigoso and Muggiano (La Spezia, Italy). Then, it was towed to Norway (VARD Langsten Shipbuilding) for final outfitting, sea trials (equipment tests) and official delivery to the shipowner Norsk Polarinstitutt ()Norwegian Polar Institute).
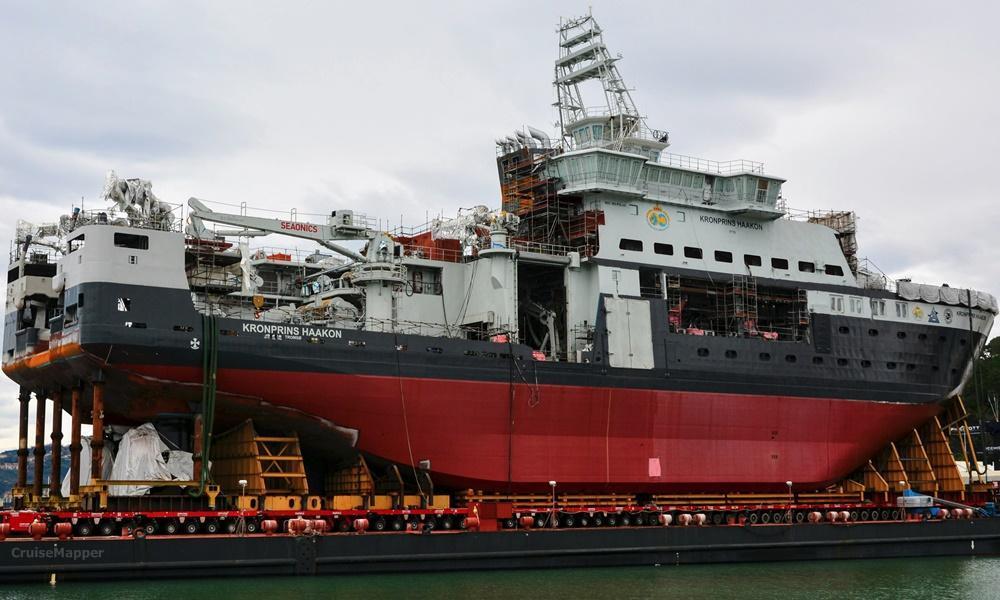

The ship is named after Haakon Magnus (Crown Prince of Norway, born 1973) - heir apparent to the Norwegian throne. The steel-cutting ceremony was held on June 15, 2015. The keel-laying ceremony was on September 2, 2015. The ship was launched on February 28, 2017.
On Rolls-Royce's "UT 395" project was based the company's "UT 851 PRV" polar research vessel concept (developed for the British Antarctic Survey) - the icebreaker RRS Sir David Attenborough (launched in 2019).


