MSV Nordica icebreaker
MSV Nordica icebreaker current position
The current location of MSV Nordica icebreaker is in Baltic Sea (coordinates 60.47772 N / 26.94539 E) cruising The AIS position was last reported 9 minutes ago.
Current PositionSpecifications of MSV Nordica icebreaker
| Year of build | 1994 / Age: 31 |
| Flag state | Finland |
| Builder | Aker Finnyards (Rauma, Finland) |
| Class | Finnish diesel icebreaker |
| Building cost | EUR 200 million (USD 235 million) |
| Engines (power) | Wartsila (21 MW / 28161 hp) |
| Propulsion power | 18.5 MW / 24809 hp |
| Speed | 16 kn / 30 km/h / 18 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 116 m / 381 ft |
| Beam (width) | 26 m / 85 ft |
| Gross Tonnage | 9392 gt |
| Passengers | 29 |
| Crew | 48 |
| Decks | 4 |
| Sister-ships | MSV Fennica |
| Owner | Arctia Oy |
| Operator | Arctia Offshore Oy |
MSV Nordica icebreaker Review
Review of MSV Nordica icebreaker
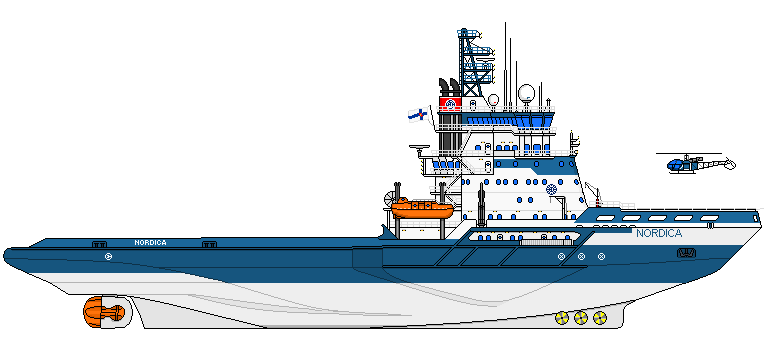
MS Nordica is a Finnish icebreaking vessel owned and operated by Arctia Ltd (a Finnish state-owned company). "MSV" stands for "multipurpose supply vessel". One of Finland's icebreaker ships, Nordica is a platform supply vessel specifically designed to serve offshore oil/gas platforms and other offshore construction projects. Occasionally (during winter), the ship also assists and escorts marine vessels in Baltic Sea. As an icebreaker, the ship can perform repeated ramming of ice ridges.
The vessel (IMO number 9056985) is currently Finland-flagged (MMSI 230275000) and registered in Helsinki.
With the same design is MSV Fennica and similarly-designed is MSV Botnica.
The list of other Finnish icebreakers also includes (in brackets - year built): Polaris (2016), Kontio (1987), Otso (1986), Sampo (1960), Sisu (1976), Urho (1975).
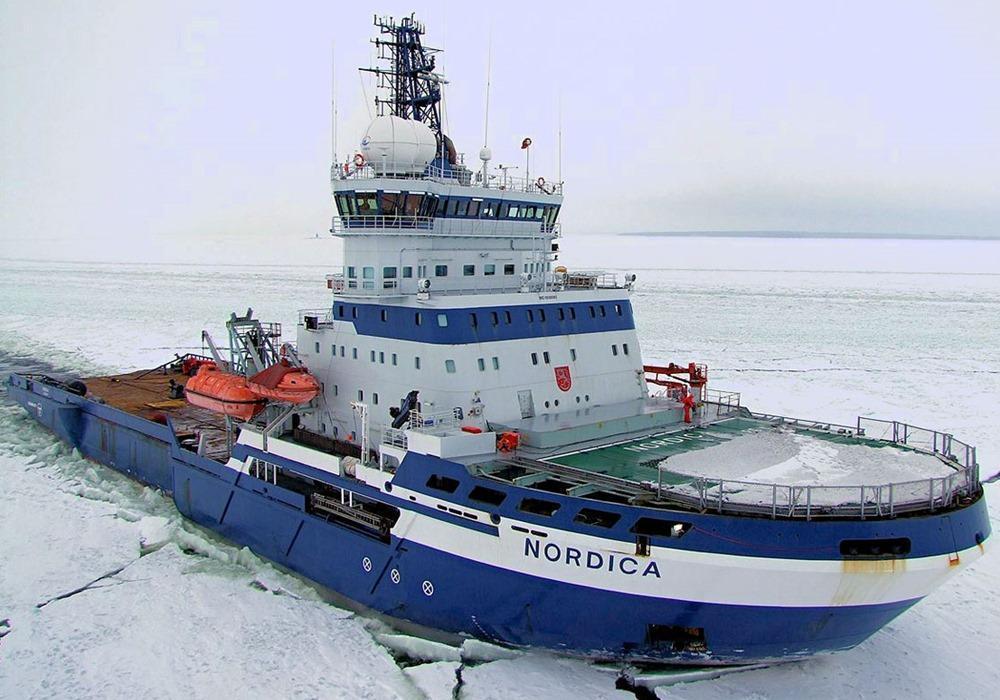

Det Norske Veritas classified the ship as "1A1 POLAR-10 Icebreaker Tug Supply Vessel". Ice class POLAR-10 signifies a hull strengthened for unassisted operations in the polar regions (the Arctic Ocean and Antarctica). According to specifications, the ship's icebreaking capacity is up to 1 m (3 ft) in conditions including glacial ice floes.
MSV Nordica was ordered in June 1992 and entered service in January 1994, following its sister-ship Fennica (launched in 1993). Back then was decided that Finland's multipurpose icebreaking ships would be privately chartered for offshore operations for the good half of each year (during Baltic Sea's ice-free period). During winter months, these vessels were planned to serve as shipping escorts.
Initially, the exclusive chartering right for both icebreakers was given to the company DSND Offshore. In 2002, it was transferred to Subsea 7 (Luxembourg-registered company specializing in subsea services, engineering and construction). The exclusive right was held by Subsea 7 until 2004 when the Finnish Maritime Administration was reorganized. After 2004, the icebreaker's ownership and management were transferred to Finstaship (a state-owned company). Later, these were transferred to GDV Maritime AS (Finstaship merging with Norway-based partners). In the following period 2005-2010, this icebreaker was operated as an offshore supply vessel and not as an escort.
Nordica vessel details and technology
For better maneuverability, the ship's hull at the bow is wider in comparison to its stern section. The hull also features an explosion-welded ice belt (made of stainless steel) for reducing friction and protecting the steel plates from abrasion.
To assist offshore constructions, the ship is equipped with a Hydralift heavy-lift crane. The crane's capacity is up to 30 tons (with max radius 11 m / 36 ft) or 15 tons (max radius 20 m / 66 ft). The ship additionally has a MacGregor crane with lifting capacity 5 tons (max radius 14 m / 46 ft) or 1,5 tons (max radius 30 m / 98 ft).
Before the 2012 refit, Nordica also had a helicopter hangar (now replaced with a helipad). The ship's equipment also includes a 120-ton A-frame structure (for plows and trenching machines), Aquamaster-Rauma anchor, hydraulic towing winch and a stern notch (for towing smaller vessels through ice fields).
In late November 2014, Finland's "Cabinet Committee on Economic Policy" released an official statement regarding the country's aging icebreaking fleet. According to the statement, Arctia Shipping's old fleet will be fully replaced with new icebreakers by the year 2029. The project's overall cost is approx EURO 1 billion. The new vessels (like Polaris) must be multipurpose icebreakers (including for Arctic oil explorations).
- The vessel has 1 dining room, Sauna, no swimming pool, no elevator, 1 helipad (helicopter deck).
- Max Draught: 8,5 m (28 ft)
- DWT Deadweight tonnage: 1650-4800 tons
- Displacement tonnage: 12800 tons
- Bollard pull (emergency towing capacity) 234 tons
- Power: 2x Wartsila 16V32D diesel engines (each 6 MW power output), 2x Wartsila 12V32D diesel engines (each 4,5 MW output)
- Propulsion: Diesel-electric, 2x Aquamaster azimuth thrusters (ABB Stromberg motors, each 7,5 MW output, with ducted fixed-pitch propellers); 3x Brunvoll bow thrusters (each 1,15 MW output, with variable-pitch propellers).
Note: In the case of poor AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's current location will be impossible. You can see CruiseMapper's list of all icebreakers and ice-breaking research ships in the "itinerary" section of our Icebreakers hub. All states and their fleets are listed there.
Other Arctia Finland cruise ships
MSV Nordica icebreaker Wiki
MSV Nordica ship's builder is Rauma Shipyard Finland.
The icebreaker's namesake is the 2000-built cruiseferry Stena Nordica.
The shipowner Arctia Oy is a state-owned company operating Finland's icebreaker fleet. The company was established in 2010 as "Arctia Shipping Oy" and was renamed in 2016 to "Arctia Oy". Arctia Ltd serves Liikennevirasto ("Finnish Transport Agency" / abbrev FTA) during winter months. This is a Finnish government agency (annual budget EUR 1,6 billion) that maintenance all the Finland's roads, railways, and waterways.
Arctia Ltd also charters the icebreaking vessels to private companies developing offshore gas-oil fields and wind farms.
Arctia Ltd has 4 subsidiaries:
- Arctia Icebreaking (managing the conventional / older icebreakers Voima, Sisu, Urho)
- Arctia Offshore (managing the multipurpose icebreakers Nordica, Fennica, Otso, and the newest - the LNG-powered Polaris)
- Arctia Karhu (managing the port icebreaking/harboring and towing service in the Gulf of Bothnia with the vessel Ahto)
- Arctia Management Services (manages the oil-recovery icebreaker Kontio)
- If necessary, all Arctia icebreakers can be equipped with oil spillage equipment.
The company's icebreaker base is at Katajanokka (Helsinki, Finland).