Sevmorput icebreaker
Sevmorput icebreaker last position
The last location of Sevmorput icebreaker is in North Russia (coordinates 69.05000 N / 33.07333 E) cruising at speed of 102.3 kn (189 km/h | 118 mph) en route to Murmansk. The AIS position was last reported 1 month ago.
Current PositionSpecifications of Sevmorput icebreaker
| Year of build | 1988 / Age: 37 |
| Flag state | Russia |
| Builder | Zaliv Shipyard (Kerch, Ukraine) |
| Class | Russian nuclear icebreaker (container cargo ship) |
| Engines (power) | KLT-40 nuclear reactor (135 MW / 181038 hp) |
| Propulsion power | 29.4 MW / 39426 hp |
| Speed | 21 kn / 39 km/h / 24 mph |
| Length (LOA) | 260 m / 853 ft |
| Beam (width) | 32 m / 105 ft |
| Gross Tonnage | 38226 gt |
| Decks | 5 |
| Owner | Russian Federation |
| Operator | Atomflot (Rosmorport) |
Sevmorput icebreaker Review
Review of Sevmorput icebreaker
NS Sevmorput ("атомный ледокол Севморпуть") is a Russian nuclear icebreaker. "NS" stands for "nuclear ship". The vessel is state-owned (by the Russian Federation) and operated by Atomflot. The Atomflot company provides all Russian nuclear icebreakers with maintenance and technological services. The company also serves the country's special vessels fleet.
The vessel (IMO number 8729810) is Russia-flagged (MMSI 273137100) and registered in Murmansk.
Besides the container carrier Sevmorput, the list of other active Russian nuclear icebreaker ships includes Taymyr (1989), Vaygach (1990), Yamal (1992), 50 Let Pobedy (2007), Arktika (2020), Sibir (2021), Ural (2022), Yakutia (2024), Chukotka (2026), Rossiya (2027/Project Leader).
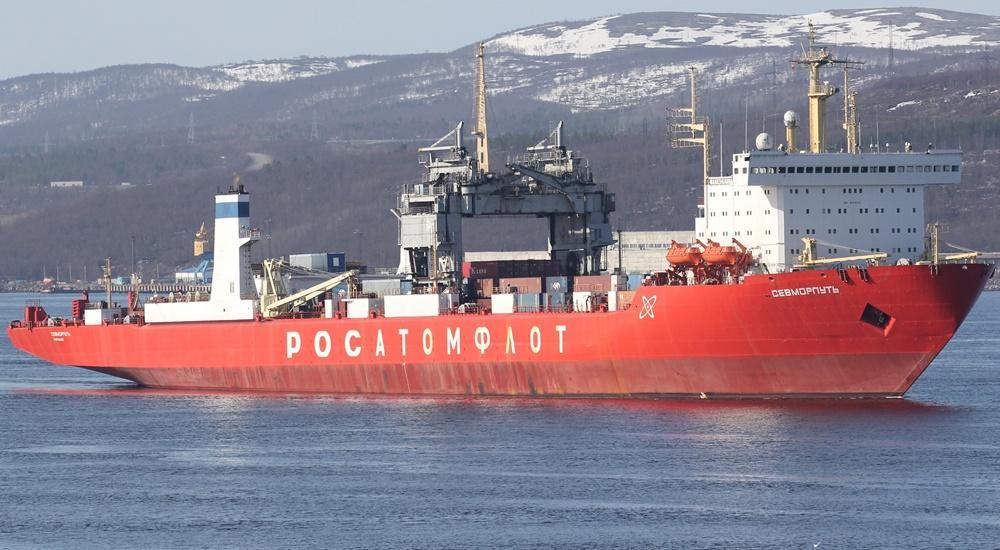

One of the largest Russian icebreaker ships Sevmorput is a nuclear-powered LASH (lighter aboard ship) cargo carrier and container ship. The vessel's building cost was nearly USD 265 million. Sevmorput is named after the Northern Sea Route ("Северный Морской Путь") on which the ship operates year-round.
In October 2012 was announced that the nuclear cargo ship would be decommissioned and scrapped. The decision was reversed in December 2013. However, as of 2015, the vessel is laid up at Atomflot base near Murmansk (Kola Peninsula, Barents Sea). Ut returned to service in February 2016.
Immediately after its launch, the icebreaker was denied entry to major seaports in the USSR Far East. Port authorities of Vostochny, Nakhodka, Vladivostok and Magadan refused to accept the 2-month-old vessel. The reason was civil protests caused by uncertainty about the safety of its nuclear power plant as the Chernobyl disaster happened only 2 years earlier (April 26, 1986). Finally, on March 13, 1989, Sevmorput was allowed to dock at Vladivostok.
The ship was used mainly on the cargo shipping route between Murmansk and Dudinka, but also made several sailings to Vietnam. As of 2016, the Sevmorput icebreaker's itinerary program offers services as a floating laboratory resource support for the Arctic.
Russia's nuclear fleet of ice-breaking vessels is used exclusively in the Arctic Ocean for escorting merchant ships and assisting research stations floating in the ice-covered waters north of Siberia. These ships are also used for scientific and Arctic cruise expeditions. The Russian nuclear ice-breakers must sail in ice-cold waters to effectively cool their reactors.
NS Sevmorput container ship details
As cargo capacity, Sevmorput can carry 74 lighters (flat-bottom barges) of 300 tons cargo capacity each, in 6 царго holds and in 2 layers on the stern deck. The lighters are loaded and unloaded via a large gantry crane (by KONECRANES manufacturer) with a lifting capacity of 500 tons.
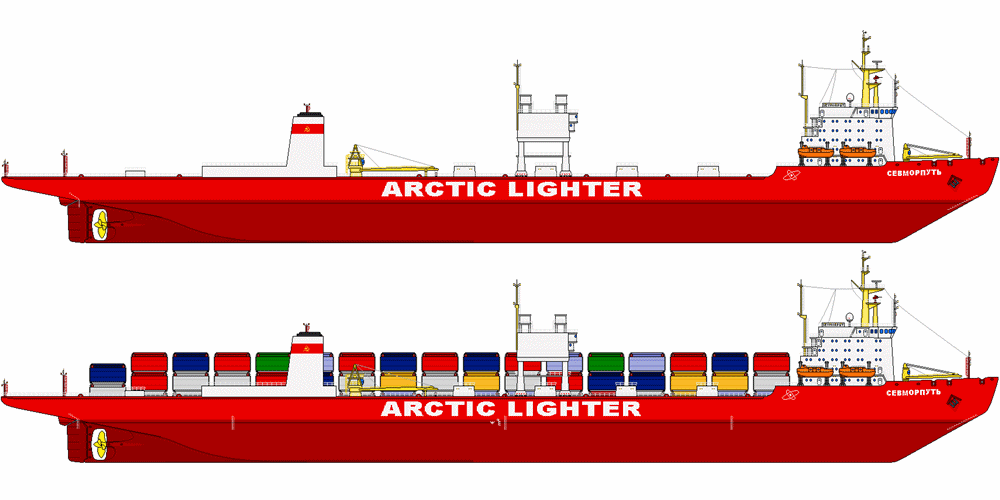
The vessel also has two 3-ton auxiliary cranes. When not carrying lighters, NS Sevmorput can carry 20- and 40-foot containers (up to 20,3 and 30,5 tons) in 3 layers. The total container capacity is 1328 TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units).
This is one of only 4 nuclear-powered merchant ships ever constructed - together with NS Mutsu (Japan, launched 1970, decommissioned in 1992), NS Savannah (the USA, launched 1962, decommissioned in 1972, currently museum ship) and NS Otto Hahn (Germany, launched 1968, scrapped in 2009).
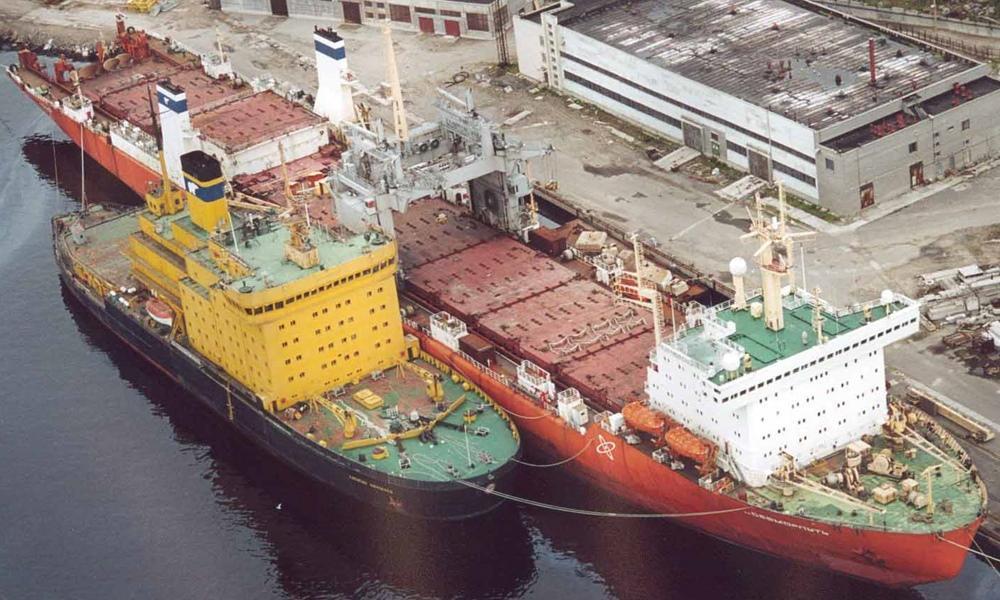

The vessel has 1 dining room, Sauna, Library, Auditorium, Passenger Lounge, Gymnasium, 1 swimming pool (indoor, heated), Infirmary, 1 elevator, no helipad (helicopter deck).
- Max Draft: 11 m (36 ft)
- DWT Deadweight tonnage: 26480 tons (Arctic)
- Displacement tonnage: 61800 tons
- Icebreaking capacity: 1,8 m (6 ft)
- Range: unlimited
- Powerplant: KLT-40 nuclear reactor (135 MW power output), 3x turbo-diesel generators (1,7 MW each)
- Propulsion: Single shaft; steam turbine (29,42 MW output); 1x 4-blade ducted propeller
Note: In the case of poor AIS coverage, tracking the vessel's current location will be impossible. You can see CruiseMapper's list of all icebreakers and ice-breaking research ships in the "itinerary" section of our Icebreakers hub. All states and their fleets are listed there.
Other Rosatom-Rosmorport Russia cruise ships
Sevmorput icebreaker Wiki
The vessel was laid down on November 2, 1984. It was launched (floated-out from drydock) on February 20, 1986, and inaugurated (entered service) on December 31, 1988. Ship's characteristics include nuclear power plant (total output 29 MW), DWT (displacement tonnage 61,880 tons (SLL / summer load line), SLL deadweight 33,980 tons, cargo capacity / containers 1320 (20-ft) plus 428 (40-ft).