Information on cruise ship construction and design and how cruise ships are built. Learn what is the cost of building a cruise ship, where are cruise ships built, which are the major cruise shipbuilders/yards and building companies. Plus some other shipbuilding stuff and fun facts, like who built the Titanic ship, who built the most expensive cruise ship in the world, who built the most expensive yacht in the world, who is responsible for making the best cruise vessels of the world. This survey is integrated with our cruise ship engines-propulsion-fuel and cruise safety articles.

The actual cruise shipbuilding takes 2 to 3 years (the design plans are usually started a year ahead). Shipbuilding takes place in specialized facilities called shipyards. The cruise ship hull is designed by the shipyard, while the interiors and all the special features are designed by architects. Shipbuilders (also called shipwrights) do shipbuilding, as well as ship repairs, both services being also referred to as "naval engineering". The reverse process (dismantling of ships) is called ship breaking/demolition. The world's biggest ship-breaking scrap yards are in India (Alang), Bangladesh (Chittagong), Pakistan (Gadani), and Turkey (Aliaga).
Cruise ship construction and design
The cruise shipbuilding process involves numerous complex research and testing procedures. The cruise ship design company (whose work is also called naval architecture) analyses and provides solutions to meet the Marine and Shipbuilding Industry's requirements, submitting the basic and detailed designs, ship equipment designs and production drawings to the shipbuilding company. The design firm also provides engineers with analysis, simulations, diagnosis, manufacture, repair and other data by using the latest CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) technology. The ship cabins manufacturer is able to design and produce various types of ready-to-install ship cabins and bathrooms for virtually all passenger ships - big and small, luxury, ferries, Ro-Ros, research, etc. The shipbuilder also hires a company to provide the so-called "Lifecycle Services", pertaining mostly to the industry's rules and regulations. Some of these services are retrofitting and refurbishing and keeping regular updates regarding new rules and requirements.
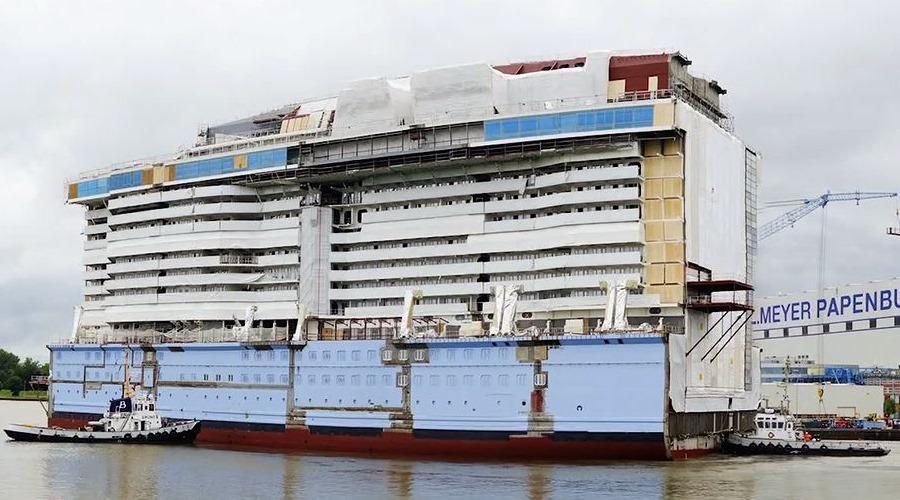
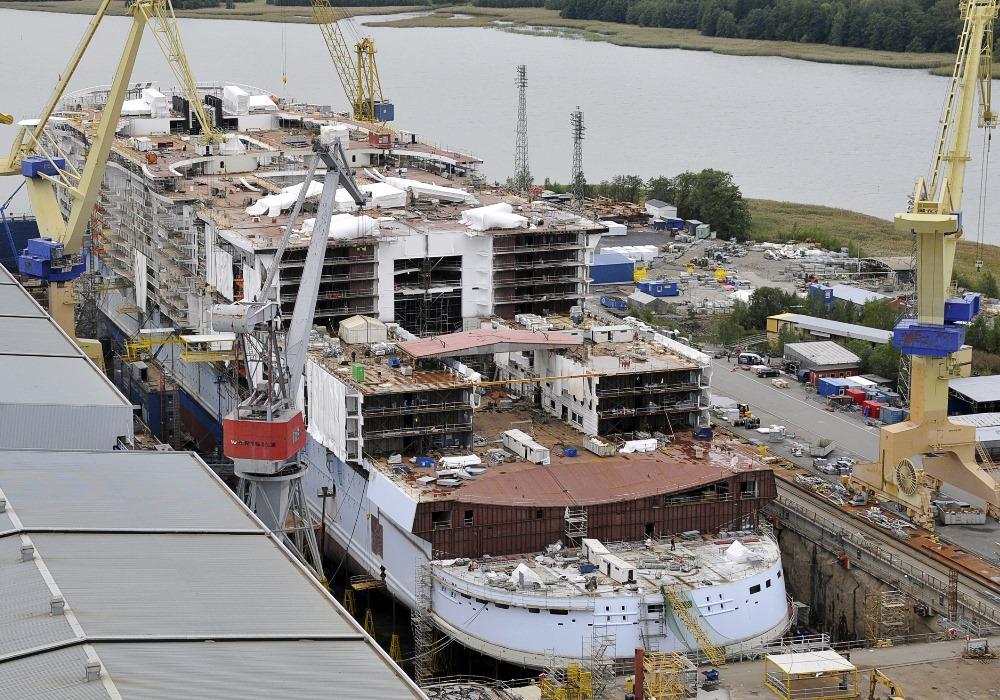
It's a common modern practice big cruise ships to be built of pre-made huge sections. Entire multi-deck segments are built at another place, transported or slipway to the shipyard and lifted into place. The sections often feature even pre-installed equipment, cables, pipes, and other components - it saves a lot of shipbuilding time, and it surely saves lots of money. This technique was used for the first time in the construction of Cunard's Queen Mary 2 (2002-2004) by the French "Chantiers de l'Atlantique" company.
The next photo shows a pre-made section for the Symphony Of The Seas ship construction.

The ice-going cruise shipbuilding is so expensive as to hull strength and engine power, that the best option is to buy an unfinished vessel or to refit an existing Ice-class ship (often an ex-navy vessel), like the case of the Regent Seven Seas Navigator ship. Constructed as a naval support ship and strengthened for navigation in ice, the Navigator ship's hull was purchased from the former USSR (now Russia), while its superstructure was finished later at the T. Mariotti shipyards in Genoa, Italy.
The following YouTube timelapse video shows the Japan-made AIDAprima cruise ship construction process (shipyard Nagasaki Japan). Next YouTube video shows the Aqua Mekong riverboat construction (time-lapse).
Cruise ship design
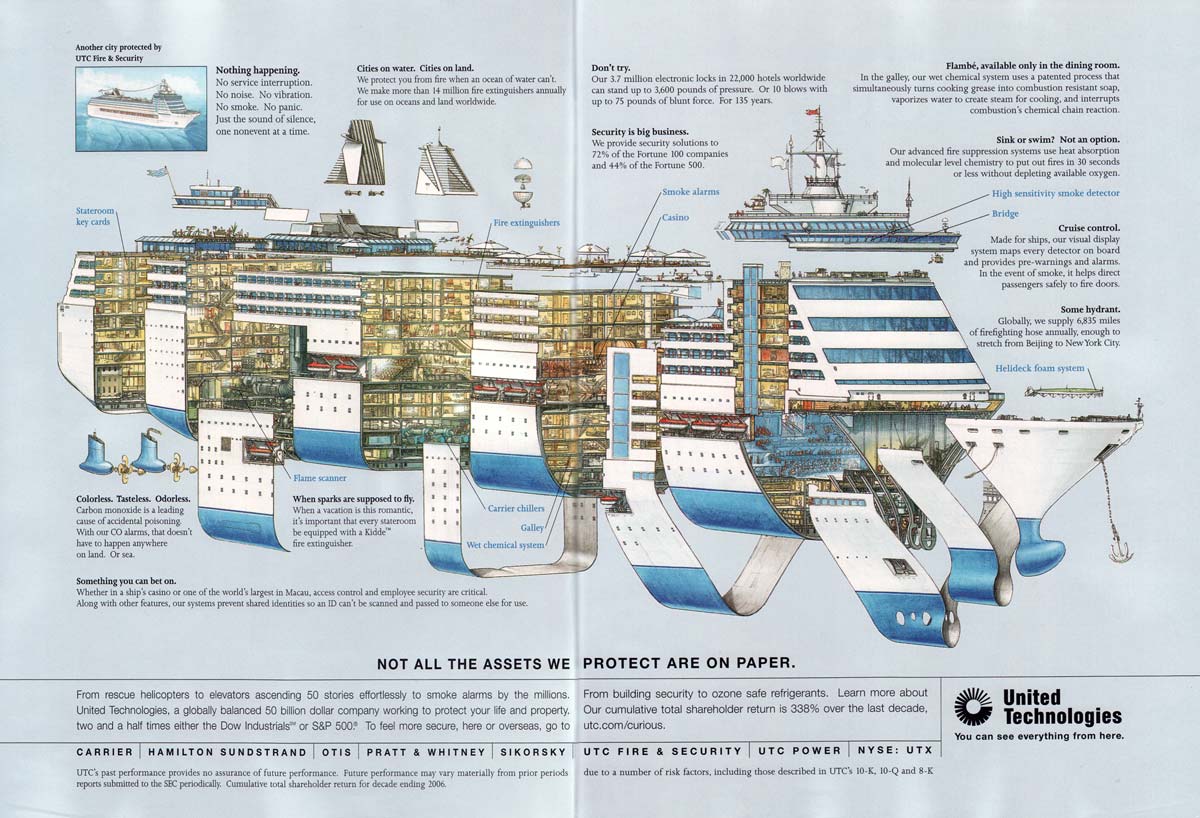
This is an amazingly detailed cruise ship design infographic showing what is what and where on a typical cruise passenger vessel. Note: Click on image to enlarge, backspace/back button to return to the article page.
Marine design solutions for cruise ships are truly amazing and unique, using the latest innovations, technologies, and materials to ensure difference from other existing passenger ships. Special onboard features, such as the Royal Caribbean ships' rock-climbing walls, ice-skating rinks, surf simulators, wave pools, and the 9-deck high Zip-line are an irresistible temptation and a true allure for all the ship vacation fun fans. As to the common features, all big-capacity passenger ships have a several decks-high Atrium, at least 3 huge swimming pools, a Spa-Fitness complex, a grand casino, a library, duty-free shops, 2 huge capacity main restaurants, grand theatre, disco nightclub, kids and teen areas, numerous bars and lounges, and all-new big ships feature an open wraparound Promenade.
Cruise ship interior design
What about cruise ship interior designs? An example is SMC Design, which was appointed by Cunard Line to lead the development of the interior spaces on RMS Queen Mary 2 in preparation for liner's drydock refit in 2016. Cunard's flagship had a multi-million 25-day extensive refurbishment (May 27-June 21, 2016) that boasted new interior designs. The most iconic liner in the world opened the next chapter in her illustrious career. The announcement of the designer company followed the news that QM2 will gain 15 brand new single cabins and an additional 30 Britannia Club rooms during the refit. The popular onboard kennels were expanded in order to cater to the high demand this extraordinary facility already attracts.
SMC Design was established in 1994. The London-based design consultancy specializes in the maritime sector. SMC Design's team has worked on many cruise vessels - from small yachts to some of the biggest ships ever built. It also has a working history with Cunard liners, leading previous refits of QE2, Cunard Princess and Cunard Countess, while also being involved in its current fleet design: Queen Victoria, Queen Elizabeth and Queen Mary 2. Andy Collier, SMC Managing Director, was part of the launch design team of QM2 at the beginning of the Century. She was then the first Atlantic liner being built for more than 35 years.
New Russian cruise ship designs
In August 2016, at Lotus shipyard (Astrakhan, Russian) part of ASC (United Shipbuilding Company), the keel was laid for the 1st Russian passenger cruise ship in decades. Support for the new class of even vessel is coming from Russian Federation president Vladimir Putin, who expressed hope that this will be the first but not the last of a series of such ships.

The Marine Engineering Bureau office engineers developed the Concept PV300VD cruise ship, the first of which is to be completed within 3 years. The project belongs to Saint Petersburg team of Marine Engineering Bureau SPb, which has been working in Russia for 16 years. Its other branch is in Odessa. Such vessels were not generally built in the old Soviet Union.

The last built in the USSR, 2 river cruise ships, Soviet Union and Lenin, were built at the Gorky plant in 1959-1960. Then, as with its ocean ships, the Soviet Union bought foreign-built river ships, until 1989-1990. However, these were not entirely foreign as they were created to Soviet order and developed for operation in Russian conditions. These vessels were built mainly in Austria, East Germany, and Czechoslovakia. After 1990, Russian riverboats were no longer built and the business was carried on for years utilizing old tonnage. The same happened with the Russian passenger fleet as they were banned in North America after Russia's invasion in Afghanistan.
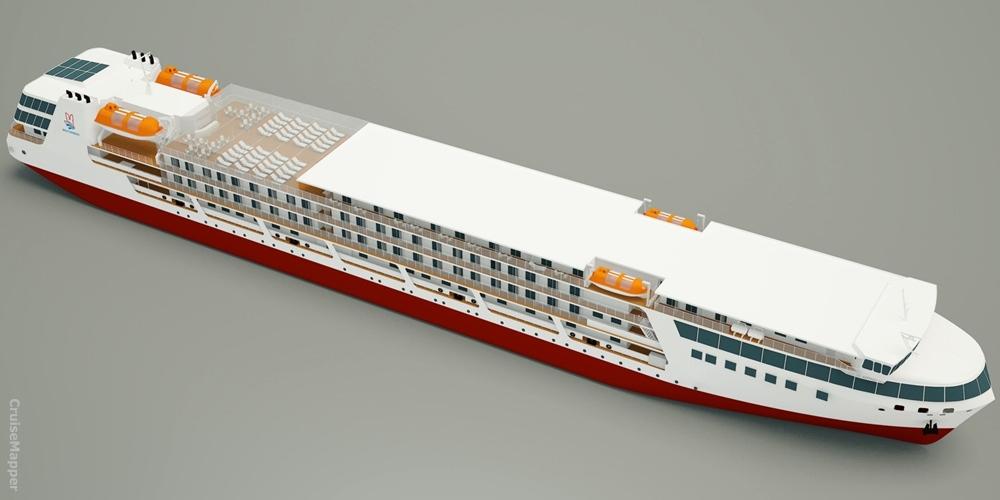

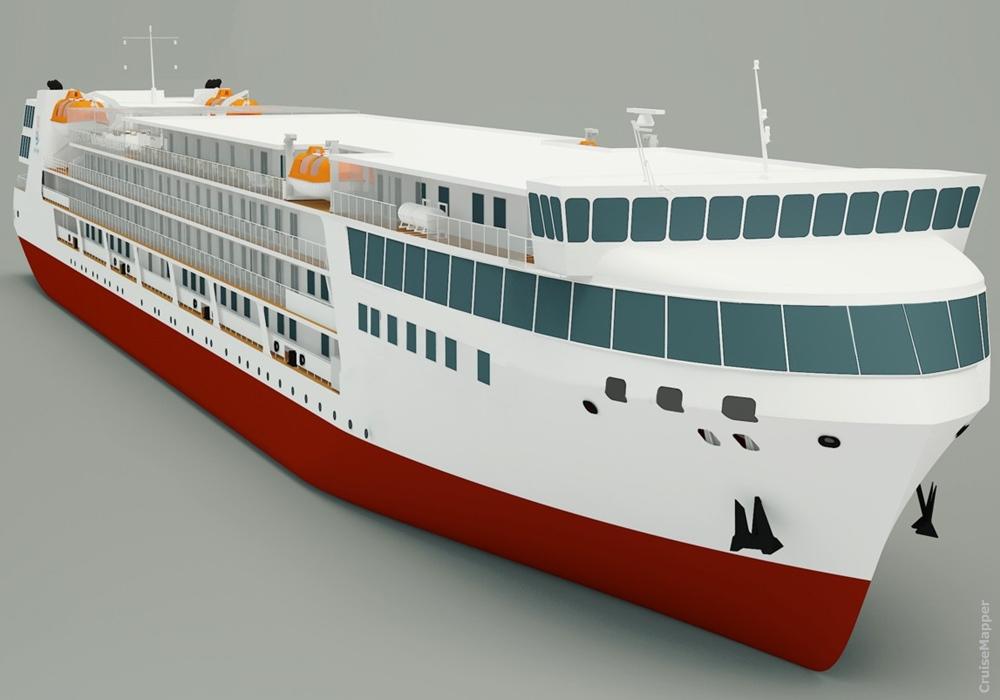
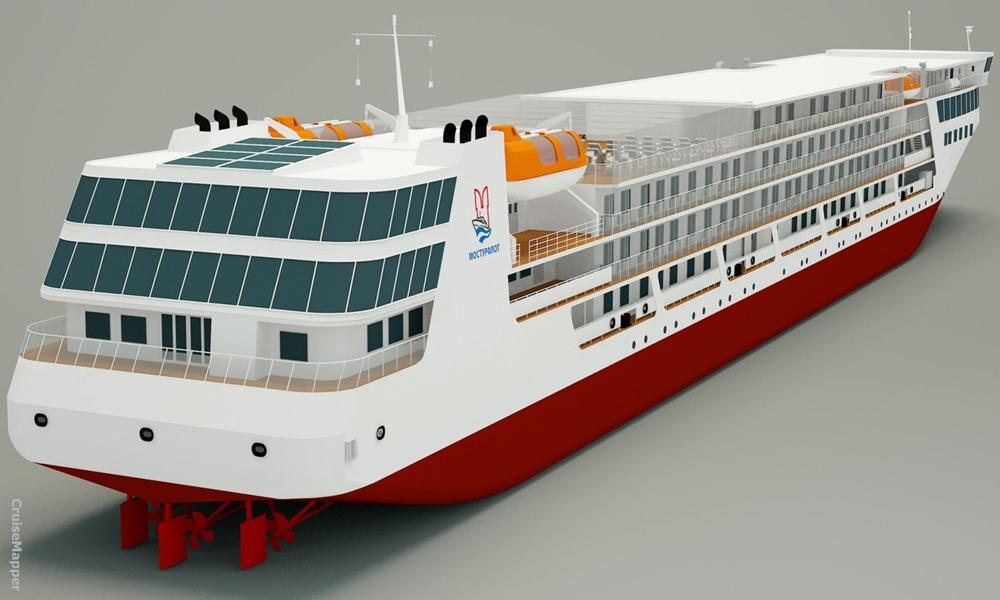
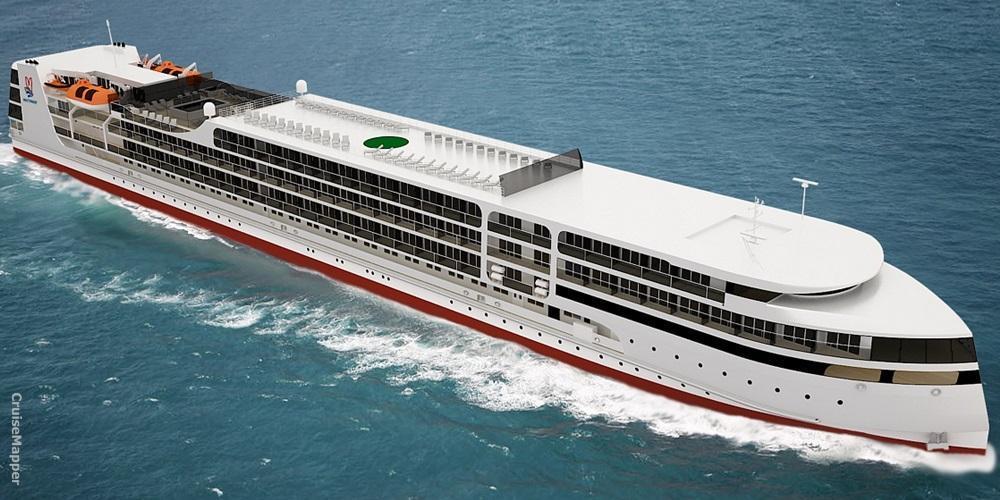
Today, shipping conditions in Russia are different. The new ships are planned to be "river-sea" ships. This class is needed in order to navigate large lakes. Russian river cruise ships are much more powerful than typical Danube and Rhine vessels. Dimensions for the new 310-passenger ships will be 463 x 55 feet. The PV300VD concept emerged in 2010-2015 by the order of the Russian Federal Marine Agency. The program's state customer and coordinator is the Minister of Industry and Trade, and completion is scheduled for 2019. The cost of a ship varies between 2.5 to 3.5 billion rubles and the payback period is 5 to 20 years. 3 such ships are foreseen at the stage, though more could follow. The next photo shows the design of Vodohod's new river cruise ship project PV300VD.

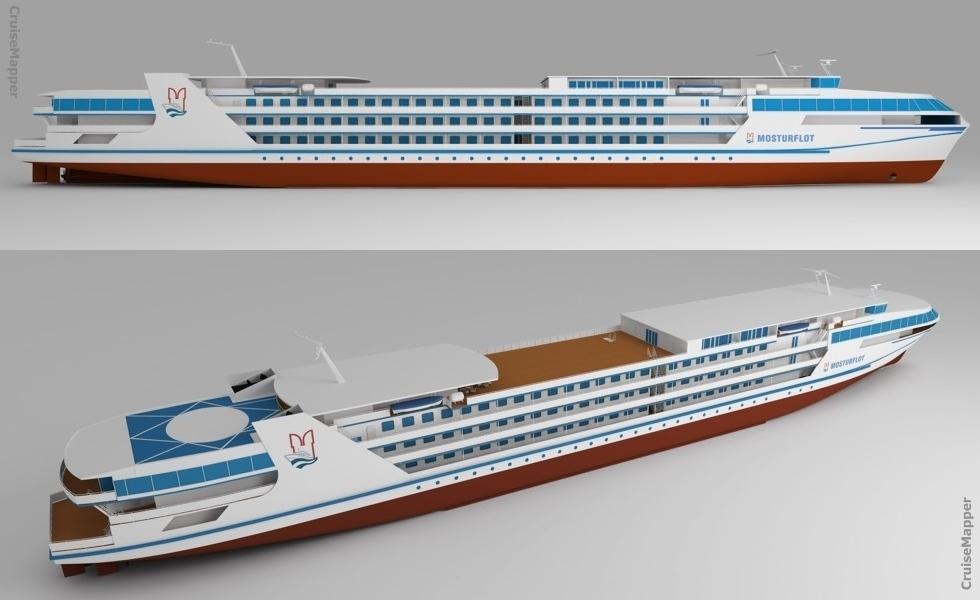
The next photo combo shows the design of Mosturflot's new river cruise ship project PV300.

The routes foreseen for the new Russian ships are in season (May to October) between Moscow and Saint Petersburg, then taking travelers from Moscow to Samara and Rostov-on-Don, in the winter embarking in the Eastern Mediterranean and possibly the Red Sea: for example, Rostov-on-Don-Yalta-Odessa-Istanbul-Alexandria. There are talks about navigation in Crimea, Sevastopol, and Sochi, on more interesting routes in the Caspian sea.
The newbuilds could carry about 500,000 passengers annually, of which about 100,000 foreign tourists. The number of foreigners declined by nearly a half in 2014 as western tour operators cut Russian programs and westerners stayed away. According to the Ministry of Industry and trade, buyers of the new ship would be operators like Mosturflot (GK Sea and River shipping company), Vodohod and Orthodox. Given the high cost of the vessels, it is planned to lease them to operators. The main difference of this 4-deck ship is that it will be able to navigate not only rivers but seas as well. The vessels will also be more luxurious than past ships and will include western amenities, such as French balconies and comfortable large suites.
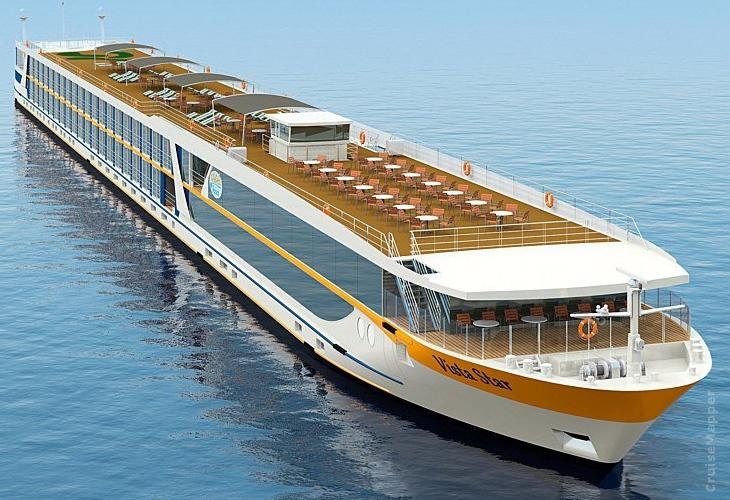
Next image shows a traditional European river cruise ship design (4-deck boat). All top-deck/sundeck structures (Wheelhouse, awnings, railings) are retractable and lowered when the boat passes under low bridges.

New expedition cruise ship designs
A new contract was awarded to the shipbuilder Uljanik (Croatia) for a 10,000-GT, 237-passenger ship (Scenic Eclipse) scheduled for delivery in 2018 but eventually postponed to 2019.
Based on these dimensions, the new ship was to be of the same general size as Ponant's fleet, the latest of which (Le Lyrial) was built at Fincantieri's Shipyard Ancona Italy. Uljanik has not disclosed the identity of the purchaser, but new ships are also expected from Lindblad and Seabourn in 2018.
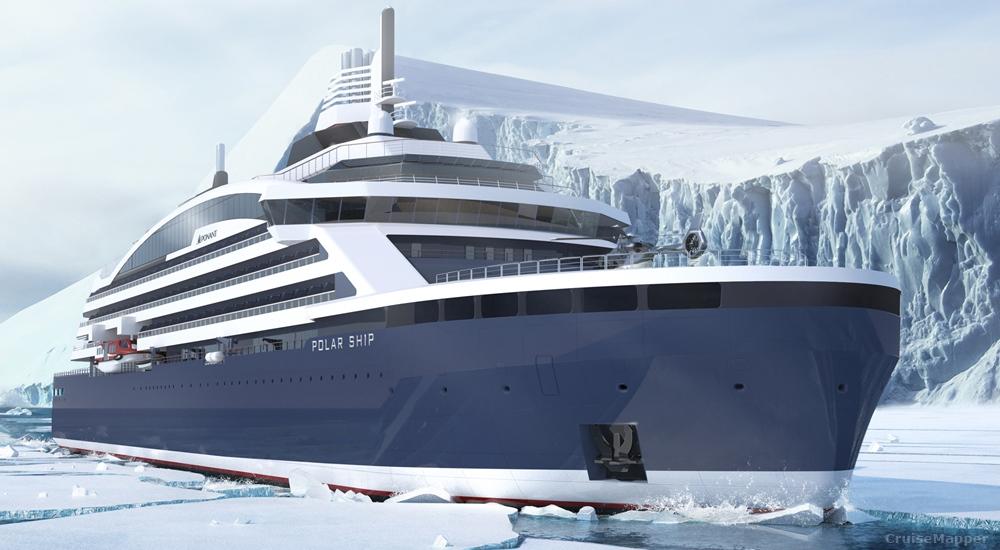
Next photos show other designs fitting the expedition vessel category.
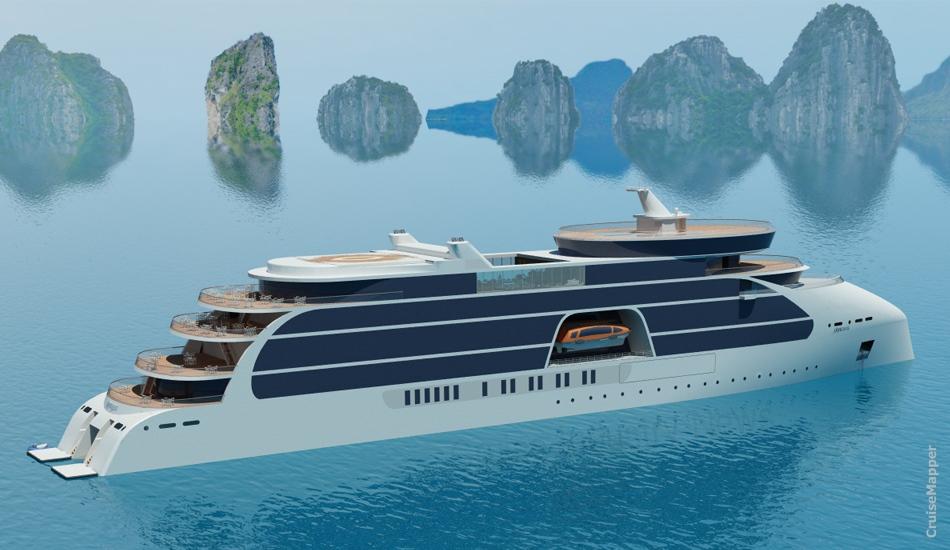

The above is STX France's Project Ulysseas (145 m length, 200 passengers) was officially revealed in March 2015.
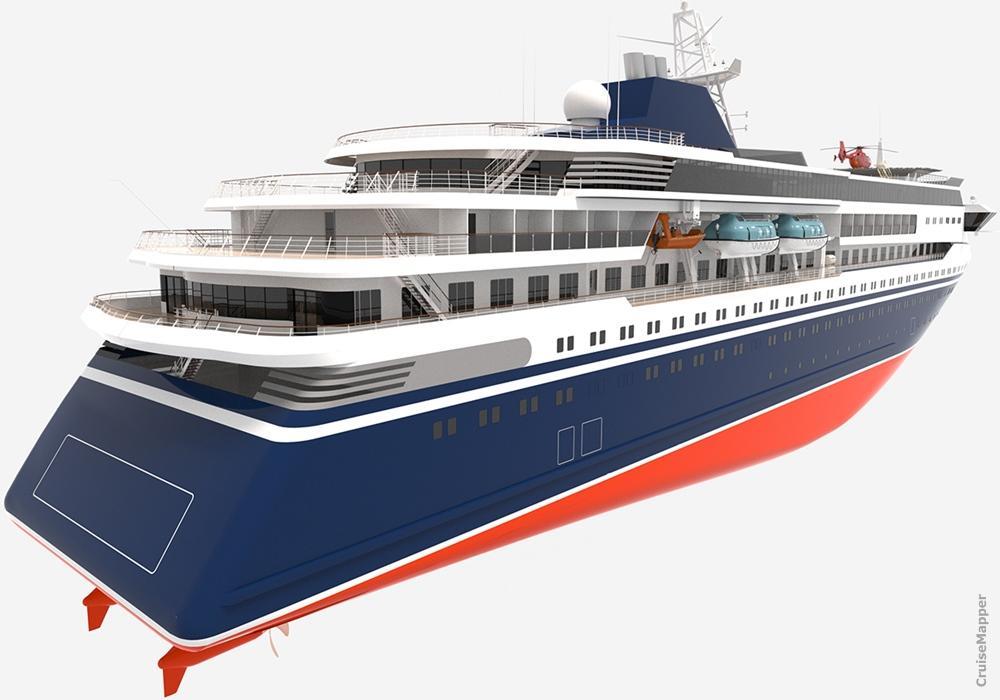
Next is the 2020-announced icebreaking cruise ship design developed by Knud E. Hansen.
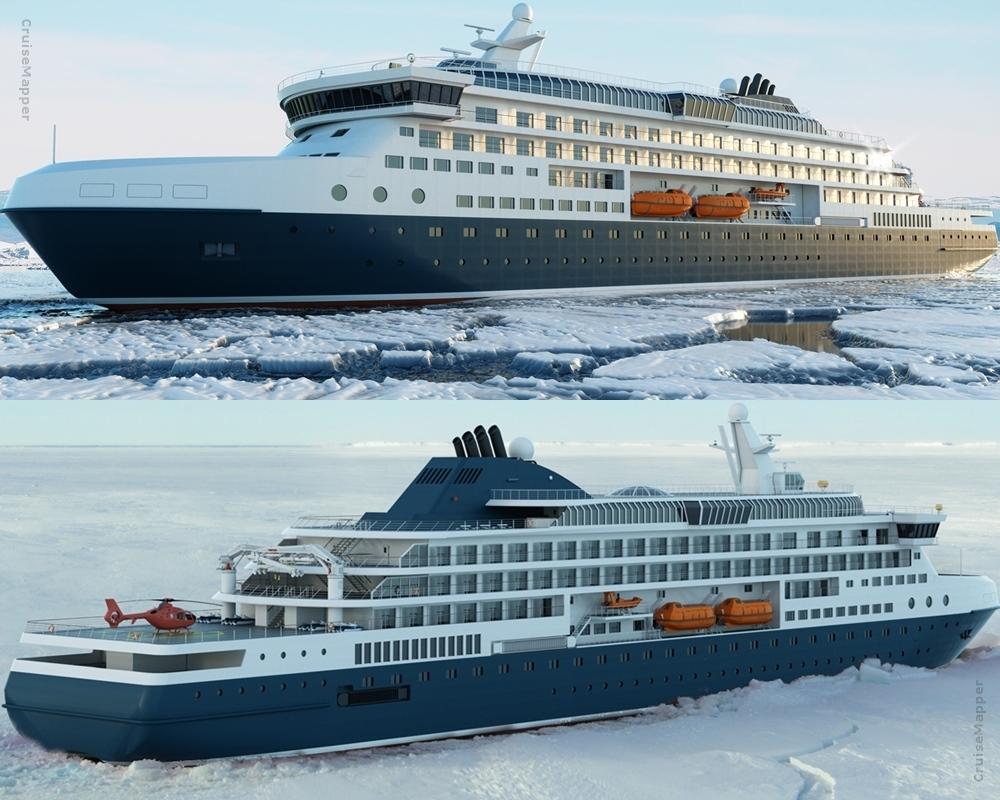

The PC3 ice-classed vessel has deadweight/DWT 1965 tons, LOA length 144 m, beam 22 m, draught 7 m, max passenger capacity 300 (plus 150 crew) and 150 staterooms. Most cabins are with step-out balconies and interconnecting, featuring the company's "Flex Cabin System" which allows their walls to be reconfigured in order to convert a Suite into two separate cabins.
The newbuild has max cruising speed 17 knots (20 mph / 32 kph), can operate in solid ice (max thickness 1,8 m) and has diesel-electric propulsion (based on 2 azipods, total power output 15 MW), 6 electricity generators (dual-fuel / LNG and MDO-diesel) plus a lithium-ion battery pack (powers the ship while docked). The new passenger ship design features an Ice Bar, multi-purpose Lounge, a tender garage (for Zodiacs and other expedition equipment that can be launched via a portside shell door), an aft-located helicopter deck (where a helicopter is lowered into the hanger on the below deck).
The next design (by Aker Arctic) is of an expedition ship ordered by the UK-based company Polar Cruise Enterprises Ltd. The vessel has LOA length of 135.5 m, Beam 17.8 m, Draught 5.5 m, Propulsion 2x 3.5 MW azimuth thrusters, Engines 4x MAK 6M32C (2,88 MW each) allowing max cruising speed 13 knots (15 mph / 24 kph).
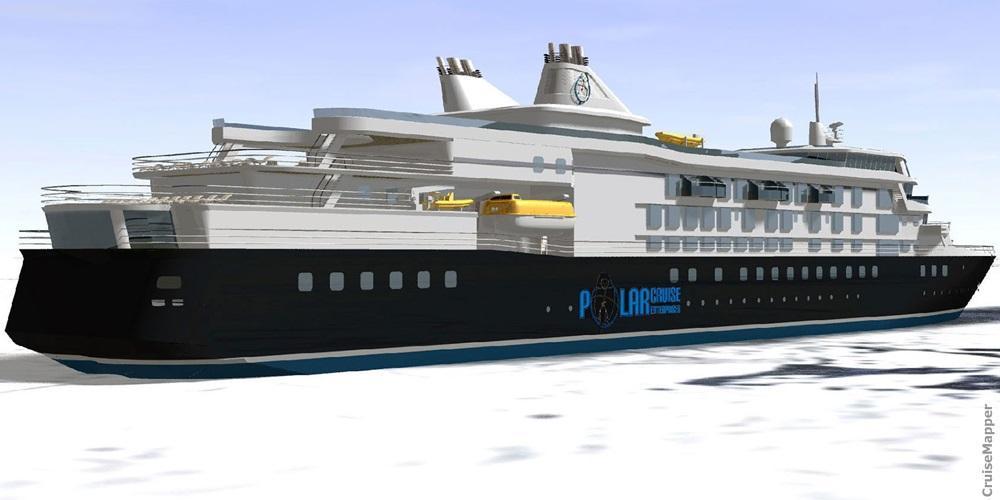

Knud E Hansen's expedition ship design is with 150 staterooms and heavy-duty, ice-rated hull.

The next video shows various passenger and research ship designs developed by Knud E Hansen (Danish marine engineering company established in 1937).
Next is the VARD-6 polar ship design on which are based the newbuilds of Ponant (Explorers-series), Hapag-Lloyd (Hanseatic-series), Viking Expeditions and Coral Expeditions (Australia).

Next images show expedition yacht cruise ship design by the Dutch shipbuilder Damen Group. The vessel is "Polar Class 6" (with ice-strengthened hull) and has endurance 30 days autonomous cruising.
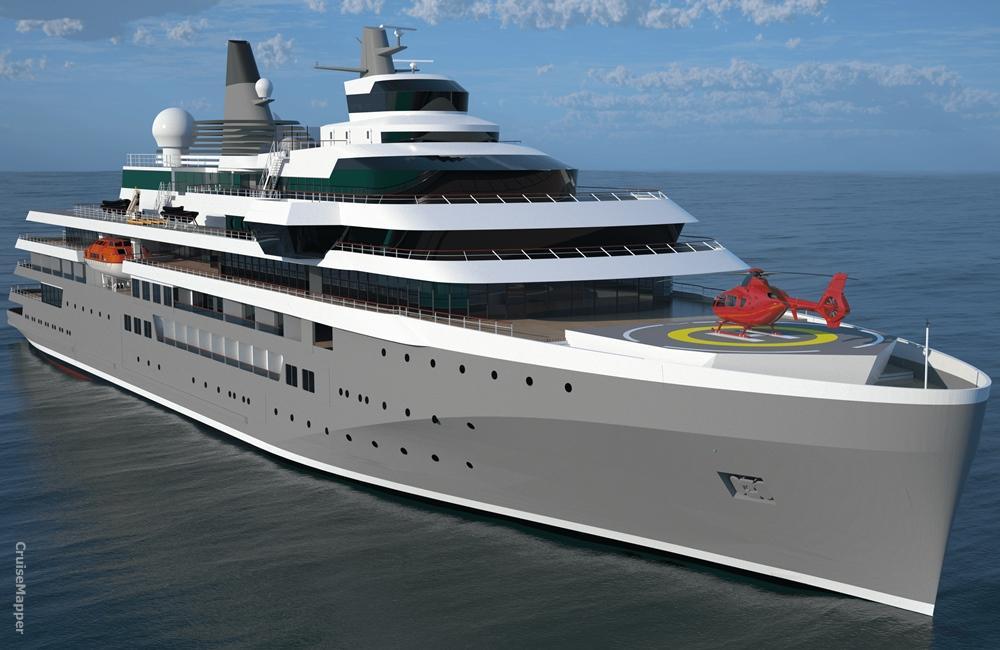

The ship has approx 1100 m2 public space and 2500 m2 outdoor deck space. Max capacity is 115 passengers. Propulsion is a diesel-mechanical hybrid and encompasses IMO Tier 3 compliant medium speed engines.
Damen Shipyards new expedition cruise ship design
Damen's cruise vessel is "battery ready", which means it could be equipped with a battery system for peak-shaving (reducing peak demand), providing supplementary power for maneuvering or silent drive operations. The hybrid propulsion is the best fuel-efficient technology currently available, allowing service speed 16 knots (30 kph / 18 mph) and max speed 18 knots (33 kph / 21 mph). The next aft view image also shows the ship's marina platform.
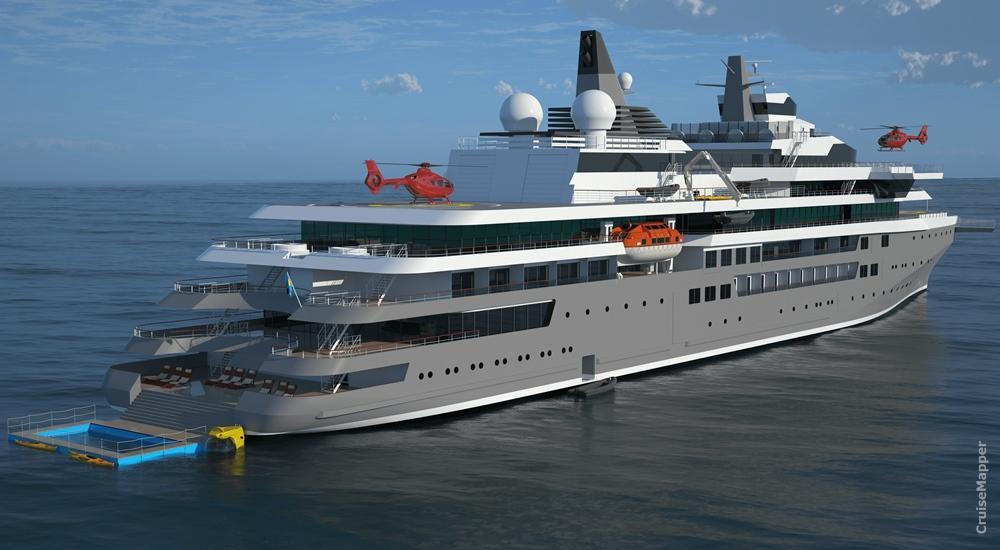

SunStone's "World-Class" expedition cruise ship design
On March 16, 2017, SunStone Ships Inc (USA) signed an agreement with the Hong Kong-based "China Merchants Industry Holdings" (CMIH) for the construction of 4 units based on the "ULSTEIN CX103" design. SunStone is currently the world's largest (by GT tonnage) shipowner chartering exclusively expedition vessels to the cruise travel industry. The contract included the option for additional 6 units.
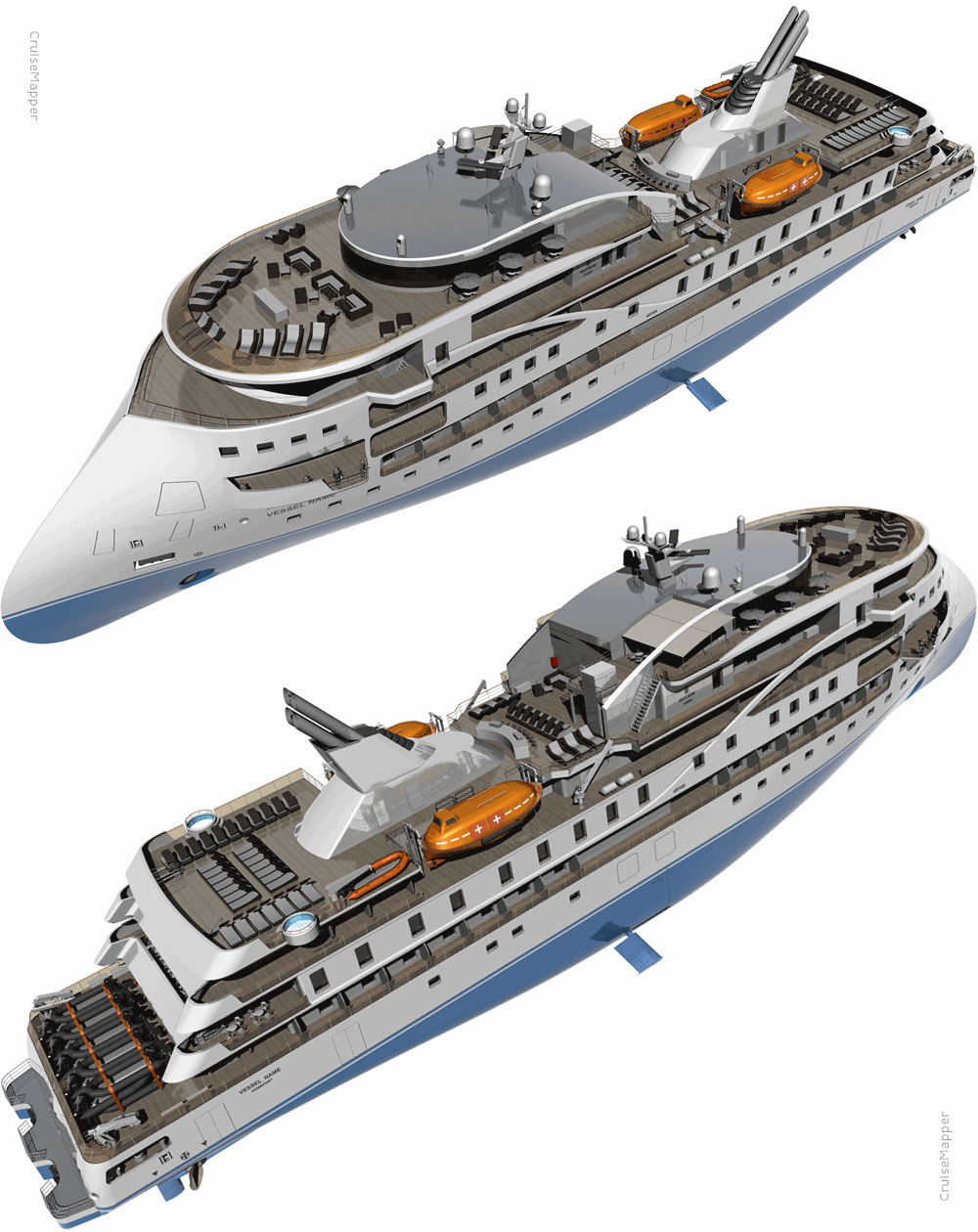
The ice-class 1A vessel has the following polar code specifications.
- Designer: SUNSTONE SHIPS INC
- Shipbuilder: (CMIH) CHINA MERCHANTS INDUSTRY HOLDINGS
- Passenger cabins: 80-95
- LOA Length: 104 m
- Beam / Width: 18 m
- Draft: 5 m
- Speed: 15 Kn / 17 mph / 28 kph
- Ice-Class: 1A
- Polar Class: PC 6 (highest)
The boat has a fleet of Zodiacs (20-22x aft-stored inflatable RIB boats) and features a dedicated Zodiac loading platform for easy boarding.
Charterers of these ships are the travel brand companies AQV-American Queen Voyages, Aurora Expeditions (fleet), Albatros Expeditions (fleet).
STX France "Ulysseas" cruise ship project
In March 2015, the major shipbuilder STX France unveiled a revolutionary new expedition ship design named "Ulysseas". It represents an innovative idea for a small cruise ship (passenger capacity 200, ice-class hull, length 476 ft / 145 m, cruising speed 17 Kn / 20 mph / 31 kph) aimed at the expedition cruising market.
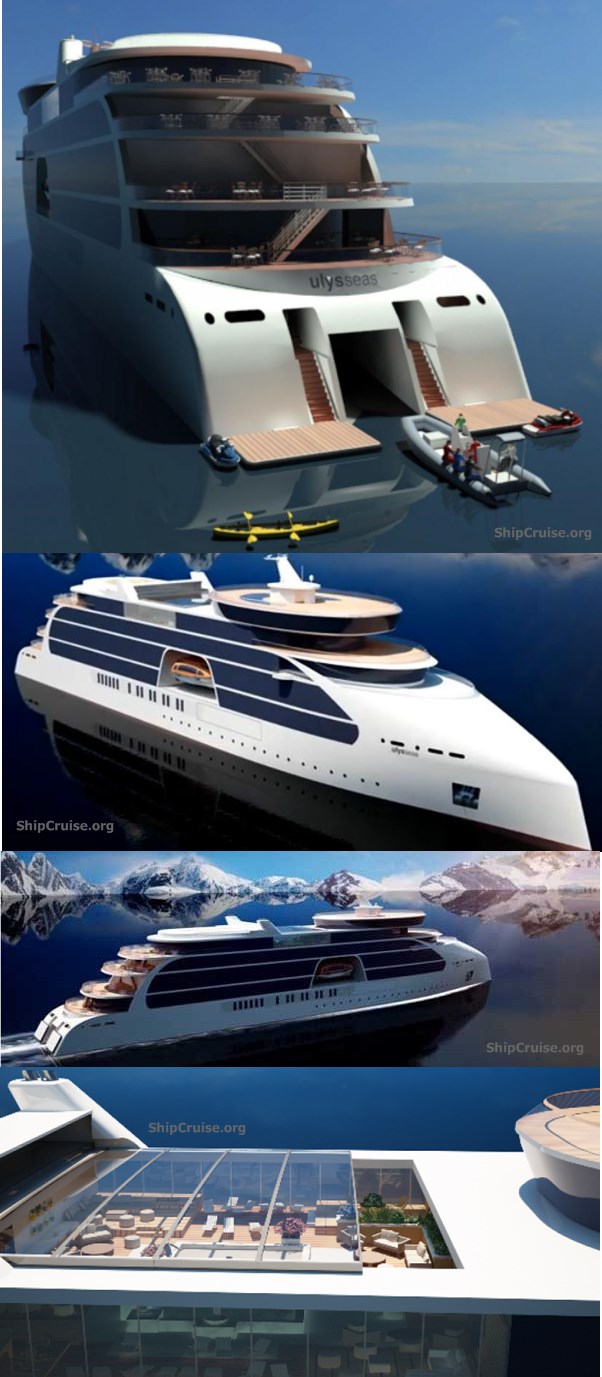

The main reason for the Ulysseas project is that currently, the expedition cruise market uses mostly second-hand vessels. Unique for this new ship design is the excessive usage of glass (in all public areas) and the French balconies (false balconies) on all passenger cabins. Every passenger-use facility on the new vessel features floor-ceiling windows. There will be a unique forward-located observation lounge for 360-degree views.
The Ulysseas ship's aft-section is an STX-patented design for saving energy. This is a movable duck-tail, which position depends on cruising speeds and weather conditions. The vessel is powered by two 2,5 MWT azipods (360-degree rotating thrusters), with 4x diesel-electric generators and 1x scrubber. This cruise ship design also features a helipad (helicopter landing pad), a helicopter storage space (inside the ship), zodiac boats for ship-to-shore operations.
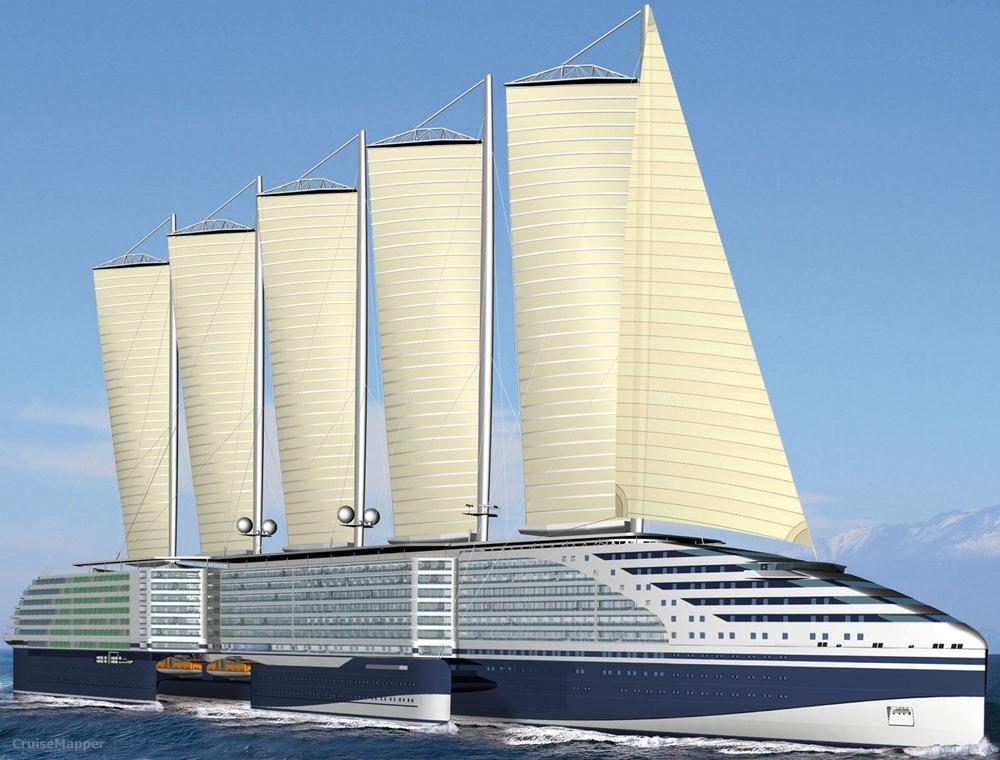
(2018) "Silenseas" sailing cruise ship design by Chantiers de l’Atlantique (fka STX FRANCE)
In early March 2018, STX France revealed a carbon-free cruise vessel design (trademarked Silenseas) using wind as main power source. The new wind-power technology was trialed on Ponant's yacht Le Ponant, on which one of the existing sails was replaced and the new technology tested.
STX France's project was something never done before. The carbon-free sailship design is an alternative to the popular hybrid-powered vessels. Hydrogen and fuel cells are still expensive, plus hydrogen is not available in most ports.
The technology uses the company's patented "SolidSail" concept. The sails (total size up to 1200 m2 / 12900 ft2) are mounted on masts but without any ropes or cables. The STX France design has 3 masts and 3 rigs, with masts rotating in order to adapt the sails to the wind. The new design also includes the latest hybrid propulsion technologies, combining wind with LNG, and potentially batteries, solar panels, and fuel cells.

The sailing ship can reach speeds of 12 knots (14 mph / 22 kph) under sail in 15 knots (17 mph / 28 kph) winds. In winds over 15 knots, the vessel's propellers will be used, acting as a turbine that draws power from the sails. On Caribbean Sea routes, the new technology could reduce propulsion energy by 60%.
STX France's sailship design was developed for 3 vessel sizes, the biggest being 15000 GT-ton with LOA length 190 m (620 ft) and 150 passenger staterooms. The French shipbuilding company started research in sail propulsion in 2009, Silenseas has technology patents (2009 and 2017) for the new sail. The unit is made from fiberglass, carbon and epoxy-resin panels.
SolidSail system debuted on October 31, 2018, on the yacht Le Ponant. The new Solid Sail (sized 300+ m2) was constructed at Chantiers de L'Atlantique (Saint-Nazaire) and installed in Marseille. The 3-masted Le Ponant departed from France to Cape Verde Islands, then embarked on a Transatlantic crossing to Cuba, testing the new sail for 1 year.
Similar is the concept of Peace Boat's new vessel Ecoship (built by Arctech Helsinki Shipyard in Helsinki, Finland).
In December 2022 was announced the shipyard's first SolidSail with a carbon-fiber mast. The project was a collaboration with the Lorient-based companies Lorima (manufacturer of carbon fiber masts and spars), Avel Robotics (manufacturer of composite parts), CDK Technologies (boat building company) and Mulitplast (Vannes-based shipbuilding company).
The carbon-fiber SolidSail mast has height 66 m/217 ft, width 2 m/7 ft and weight ~20 tons. It can carry a SolidSail sized ~1500 m2/16150 ft2.
Silenseas' SolidSail will propel the world's largest wind-powered/sailing cruise vessel - Accor's Orient Express Corinthian/fka Silenseas (2026).
Aeoldrive (rig comprising the mast and the SolidSail) is fully automated and 360-degree rotating, while the masts rotate/tilt up to 70 degrees (when the vessel passes under bridges).
(2019) "Wind Cruise Vessel" design by KNUD HANSEN
On June 19, 2019, KNUD HANSEN announced its medium-sized (LOA length 110,3 m / 361 ft) long "Wind Cruise Vessel" design. This sail-assisted ship has max passenger capacity 100, max speed 15 Kn (17 mph / 28 kph), operational range 6000 nm (6900 ml / 11100 km), draught 4,5 m (), TDW-deadweight tonnage 730 tons. The new sail-ship targets the expedition travel market and passengers who prefer destinations inaccessible by larger vessels.
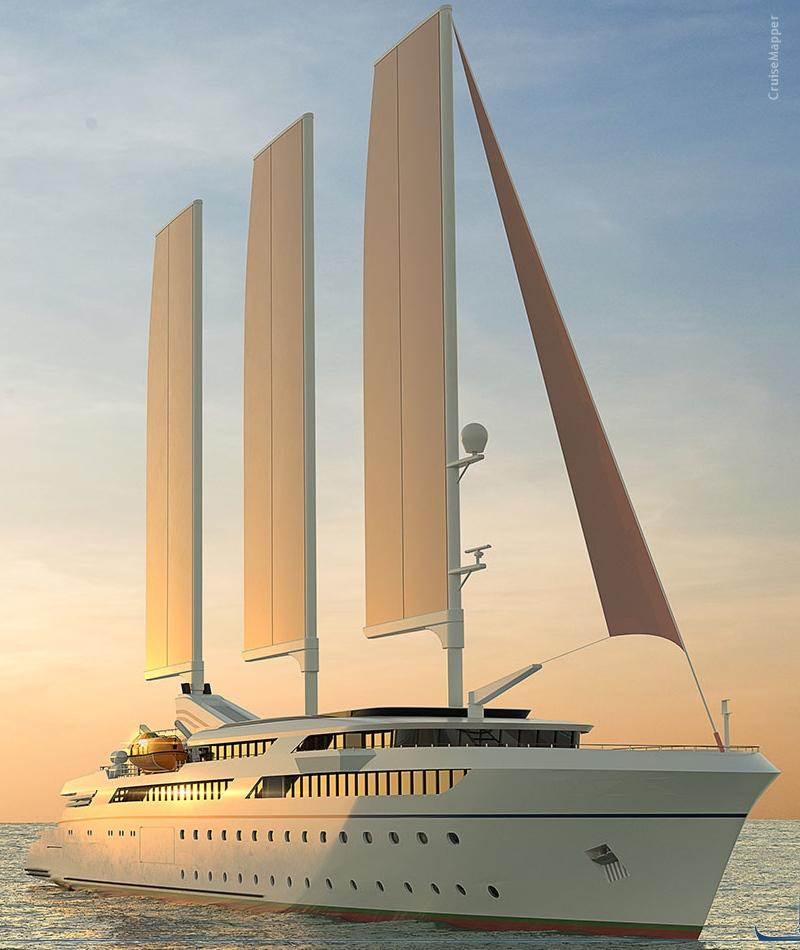

The vessel is powered by 4x low-sulfur ULSD diesel engines (plus wind power) and also includes a large battery pack (for zero emissions while in port and protected marine zones). The rig is designed by Detlev Loll Ingenieurburo GmbH (Peenemunde-based company) and comprised of 3x free-standing masts. Each mast is fitted with a fully-battened sail with adjustable flaps (wing devices that increase the max lift coefficient that a wing can generate). Ship's total sail area is 1910 m2 (20260 ft2). The sails are computer-controlled and designed for peak performance even in light winds.
The propulsion system is based on aft-located twin-screw propellers (fixed) and two fore-located tunnel thrusters (for better maneuverability in ports and anchorages). In sail-assisted mode, two fin stabilizers limit the ship's heel/listing to just 6 degrees.
Cabin decks house 48 passenger staterooms (46 cabins plus 2 suites) - all outside and many with balconies. Sea Lounge features underwater porthole windows. Deck 2 has a large tender boat garage for Zodiacs (rigid inflatable boats), jet skis, scuba diving gear, and other equipment. The ROV (remotely operated underwater vehicle) is fitted with HD camera equipment underwater observations at max depth 3 km ()9840 ft). Deck 3 is the Sun Deck featuring a swim platform with a ladder for easy water access. On Deck 4 are the restaurant (with outdoor terrace), bar, library, card room. On Deck 5 are the aft-located bar lounge and the bow-located observation area. Deck 6 has an open-air cafe and sun deck (sunbathing area with deckchairs and loungers).
Cruise ship building vs ship refurbishments
Unlike the scheduled cruise ship refurbishments, major refits may include even a cruise ship lengthening, like in the case of Royal Caribbean ship Enchantment of the Seas lengthened in 2005 (see the photo below). The Enchantment ship lengthening cost ~ US$55 million, it was a process of cutting the ship in two and inserting a whole new 73 ft (22 m) 3,500 tons midsection, pre-built at the Aker Finnyards.
The month-long dry-dock at the Keppel Verolme shipyards (Rotterdam, The Netherlands) resulted in adding 151 brand new cabins, a 50% bigger Pool Deck area, a new kids area, a teen centre, several new bars and lounges, an expanded main dining room, a new specialty restaurant. This "refurbishment cost" record was recently beaten by the CCL line and the US$155 million Carnival Destiny refit 2013 producing a brand new ship named Carnival Sunshine!
The average cost of building a cruise ship is around the US $450 for mid-sized vessels and up to $800 million for bigger cruise ships. These prices, along with the current economy status force many cruise lines to hold off from building new ships - the biggest expense of all. As a rule, all new cruise ships on order/currently under construction are by contracts signed years ago when the dollar had a good rate.
Cruise shipbuilding prices are high enough to not meet the return requirement. Even the mighty Carnival Corporation (the world's largest cruise shipowner) puts its shipbuilding plans on hold. Royal Caribbean is one of the few companies continuing to place orders for new ships - and not any ships, but the ever largest, the most innovative, the most expensive in the world. Still, most passenger ship lines are trying to keep their current fleet fresh and good looking. Two of the best examples are Holland America with its $450 million SOE program for ship renovations, and Carnival investing $250+ million to fully refit and refurbish 8 of its oldest vessels.
The next photo shows the construction of the world's largest cruise ship - Harmony of the Seas - at Saint-Nazaire (STX France).

The following tag link lists all of CruiseMapper's news related to shipbuilding.
Streets of Monaco Superyacht
"Streets of Monaco Superyacht" is a futuristic project developed by Yacht Island Design. The vessel is modeled after the actual city and designed for billionaires to sail and play.
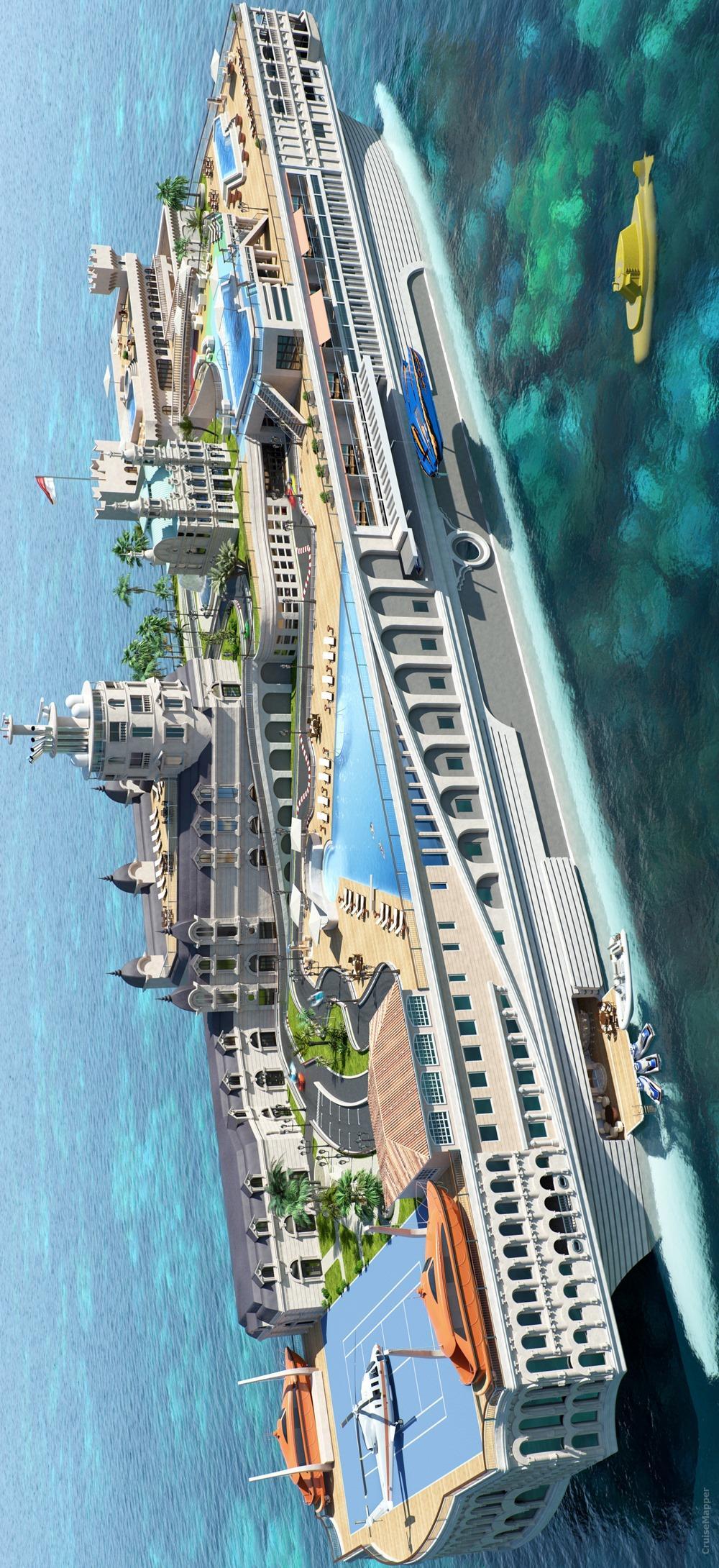

The 500-ft / 152-metre-long ship is lined with scaled-down versions of Monte Carlo's most famous buildings, including the Casino and its Grand Prix course (which on the yacht doubles as go-kart course). Among the most prominent amenities on this superyacht are swimming pools, cafes, full-service spa, full-size sports court (doubles as a helipad for private helicopters), library, interior parking for smaller boats, mini-submarine.
Staterooms (1VIP Suites) are sized 3800 ft2 (350 m2) each. There are also cabins for the 70 crew and staff members. The Superyacht cost about USD 1 billion.
Havyard's sightseeing cruise vessel design
In July 2019, Havyard Group ASA (Fosnavag Norway-based ship technology company) and SINTEF (Trondheim Norway-based research company) started a project for designing a new environmentally friendly sightseeing cruise vessel specifically for touring the Norwegian Fjords, as well as a new Norwegian Coastal cruiseferry design. The project includes measuring energy consumption, hull optimization, developing new-generation equipment and using renewable energy sources.
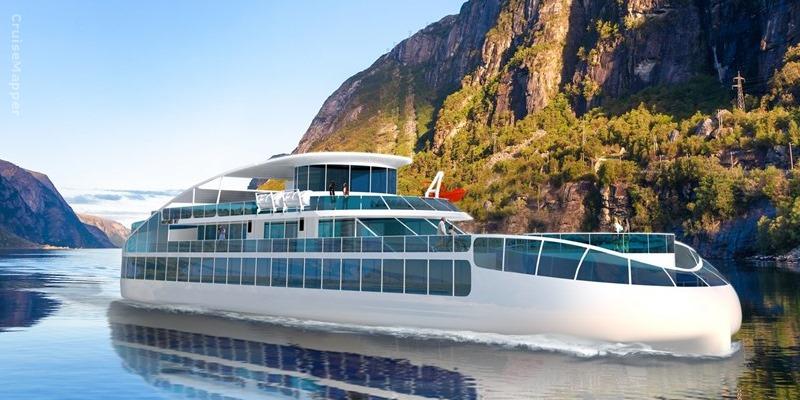

These ships are designed with battery-power propulsion (zero-emission) and recharging in call port. The vessel has LOA length is 70 m (230 ft), max passenger capacity between 600-800, max speed 10-11 knots (20 kph / 13 mph), floor-ceiling and wall-to-wall windows throughout (for unobstructed fjord cruising experiences), wheelchair-friendly interior and exterior spaces. The new vessel's designer is Stig Magne Espeseth.
Passenger embarkations/debarkations are at floating hubs (platforms at sea) installed at the fjord's mouth and outside the itinerary's seaports. The hubs also double as charging stations for the smaller-sized vessels.